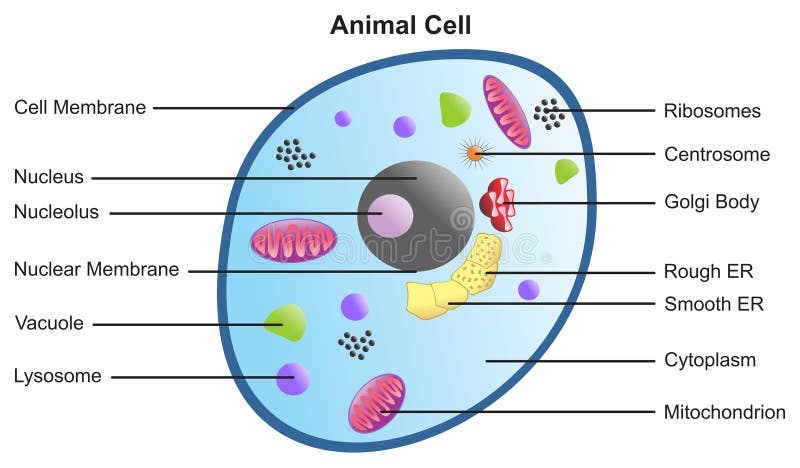
44 parts of the animal cells
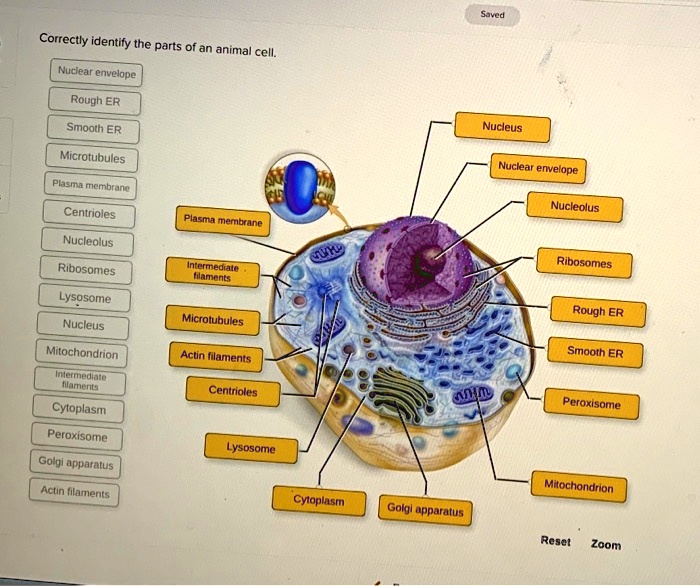
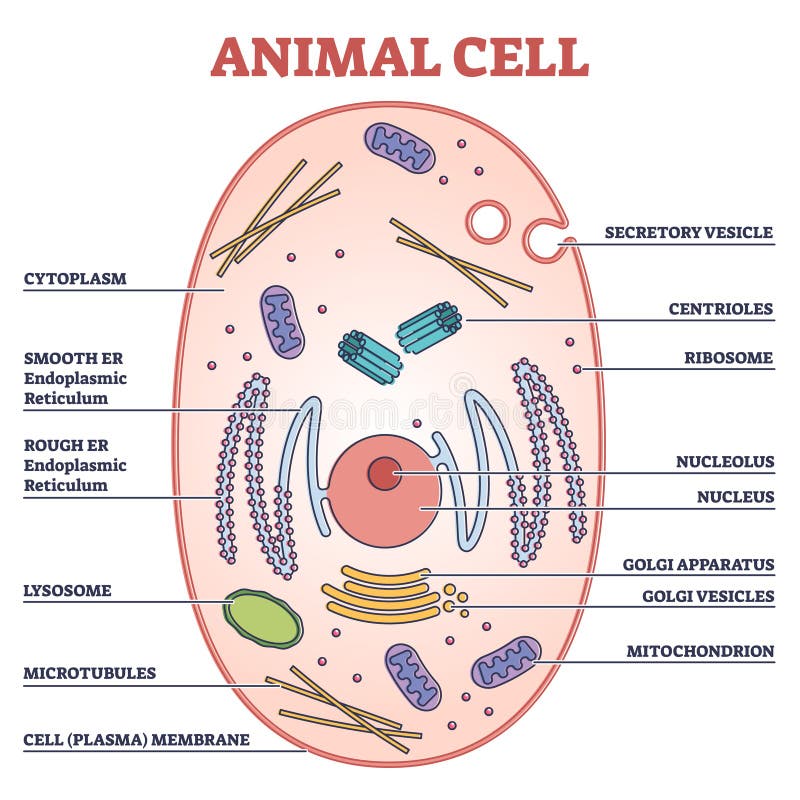
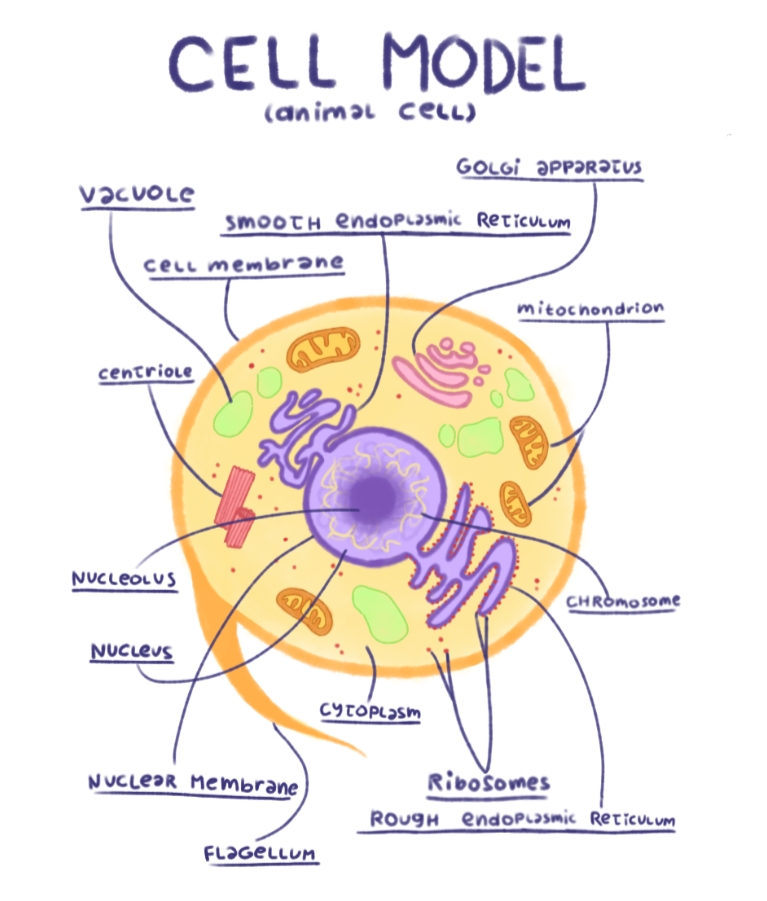
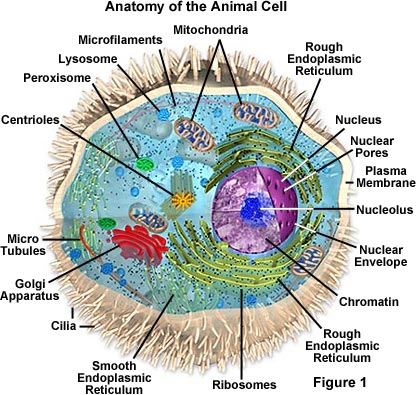
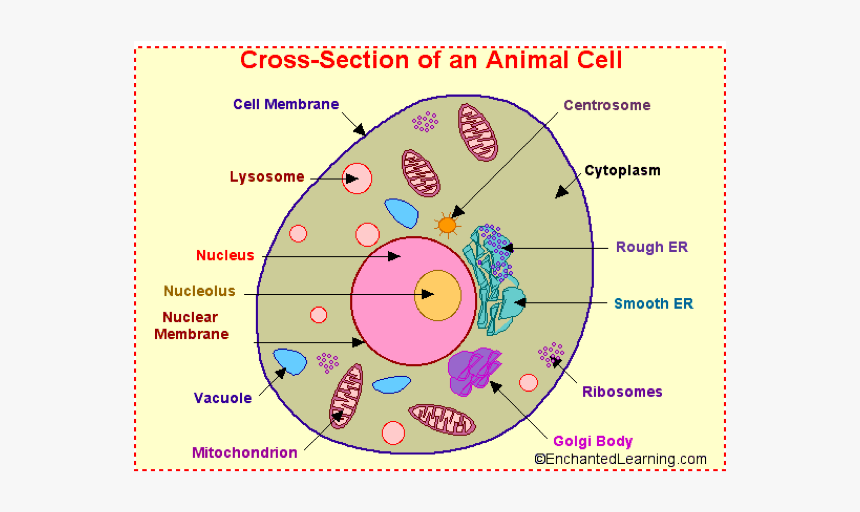
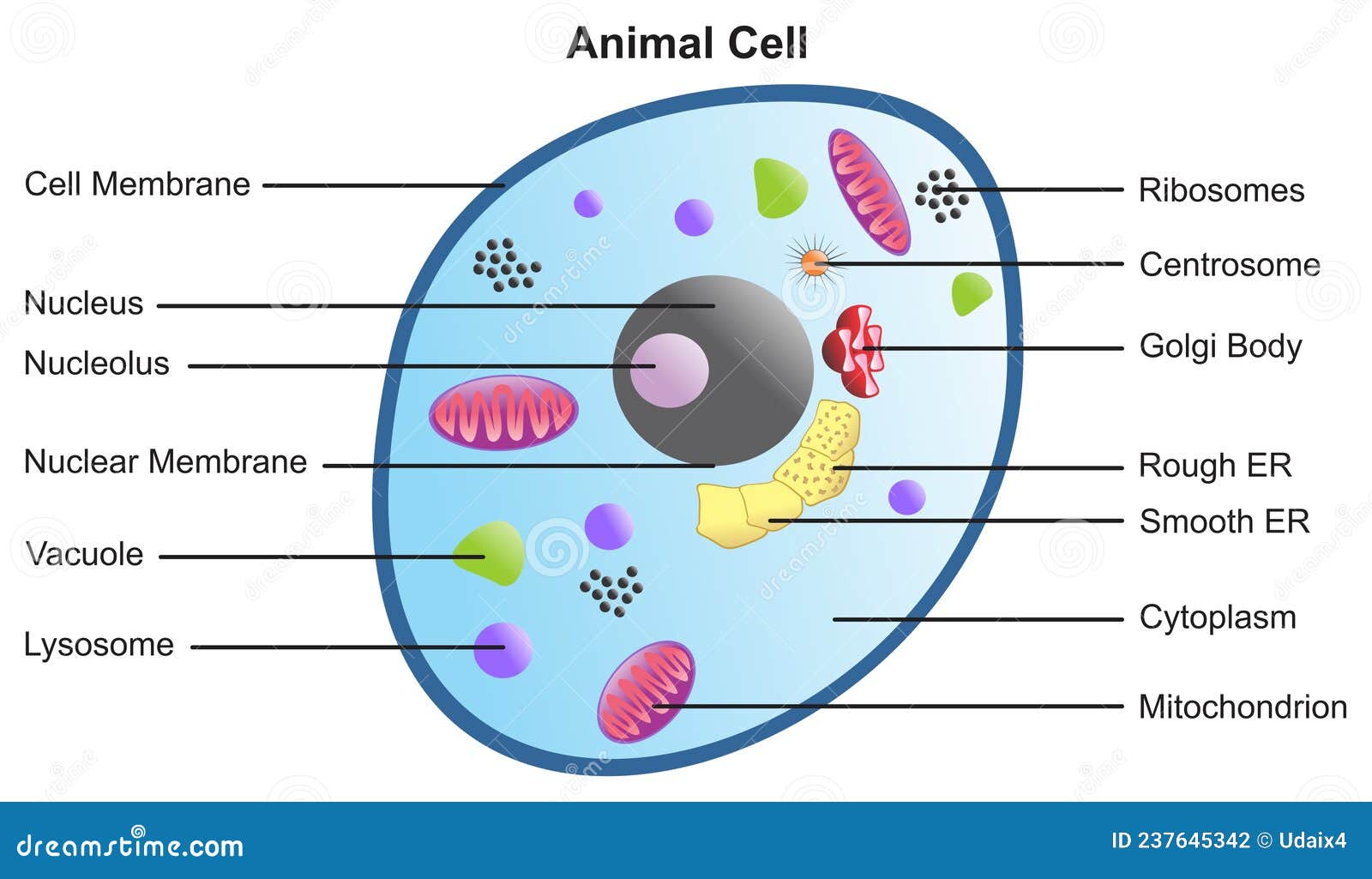
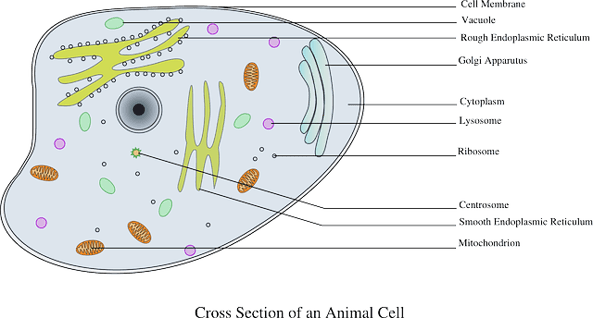
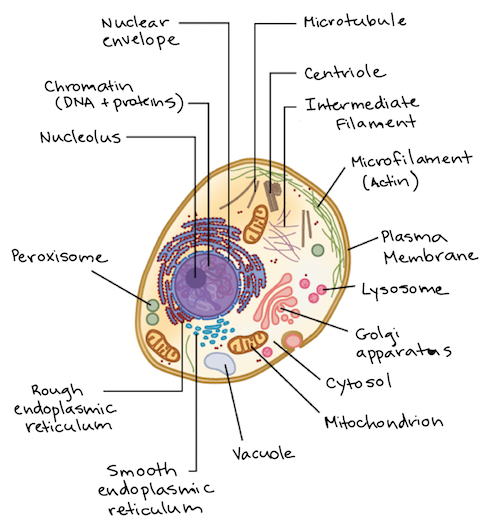
Cell Parts and Functions | Biology Dictionary Plant and animal cells both contain organelles, many of which are found in both types of cells. However, there are some organelles (such as chloroplasts, the cell wall, and large vacuoles) that are only found in plant cells. Plant and animal cells contain subcellular structures called organelles Animal Cell Parts And Their Functions The Parts Of An Animal Cell - Science Trends There are 13 main parts of an animal cell: cell membrane, nucleus, nucleolus, nuclear membrane, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, mitochondria, centrioles, cytoskeleton, vacuoles, and vesicles.
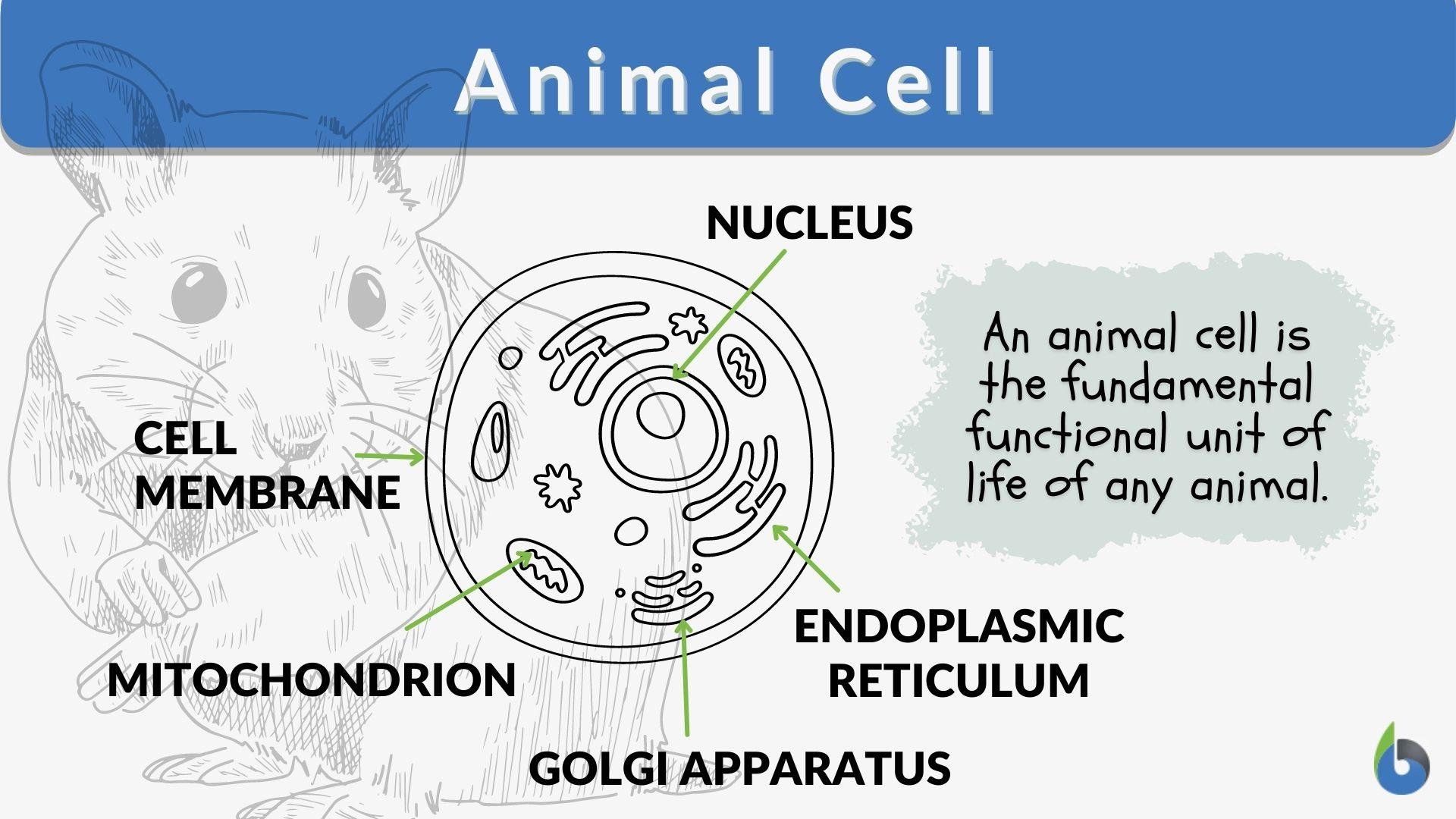
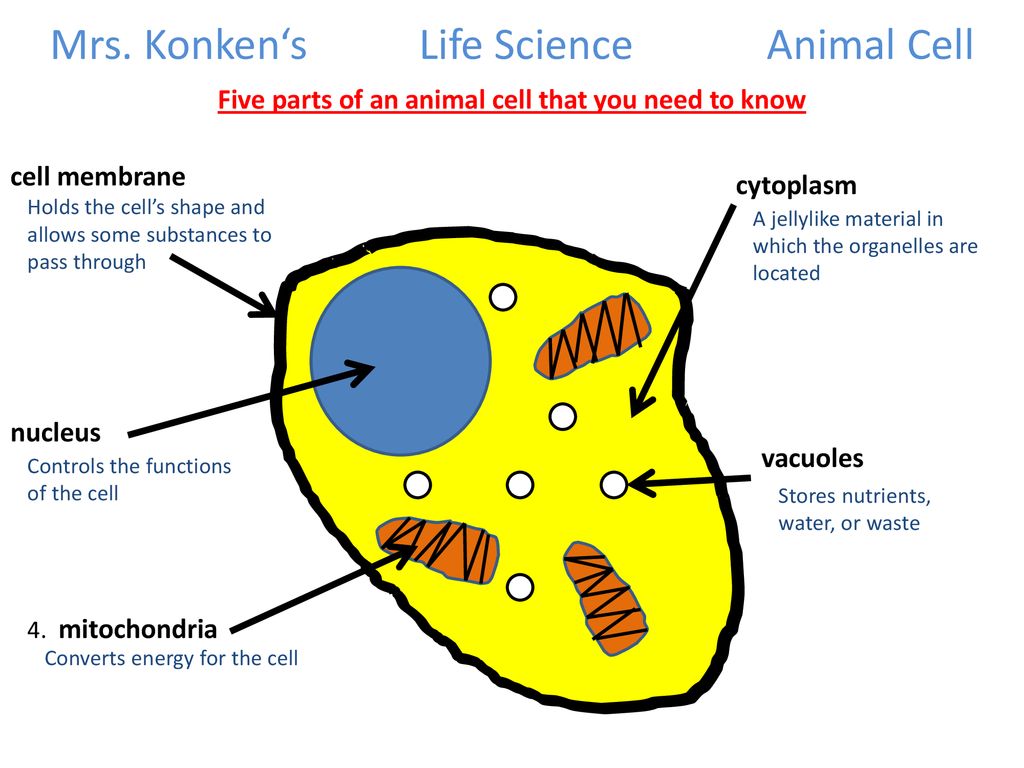
How Does the Animal Cell Work? Learn About the Functioning of a Cell in ... Three Basic Parts of the Cell. The animal cell is made up of three basic parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus and protoplasm. Consider the cell membrane as the gatekeeper. It surrounds the cell contents and separates the cell from other cells and from the external environment. Nothing gets in or out without permission from the nucleus.

Parts of the animal cells
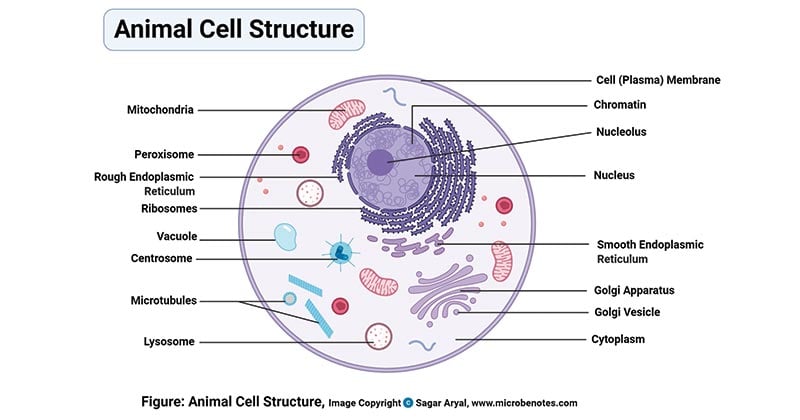
A Quick Guide to the Structure and Functions of the Animal Cell An animal cell is the smallest unit that makes up the varied tissues of animal species. There are hundreds of cell types in a developed organism, which are specific to their location and function. The red blood cells make up the blood, while the nerve cells make up the nervous system tissues. Likewise, there are more than 200 types of cells in ... 15 parts of the animal cell Flashcards | Quizlet Cytoplasm This is the area that contains the important structures of the cell Ribosomes These are the 'factories' where proteins are put together, these are also inside the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Vacuole The 'warehouse' of the cell where materials are stored Mitochondria These are the 'power plants' of the cell where energy is made Chromatin Animal Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram List of Animal cell organelles Plasma membrane (Cell membrane) Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Golgi apparatus (Golgi bodies/Golgi complex) Lysosomes Cytoskeleton Microtubules Centrioles Peroxisomes Cilia and Flagella Endosome Vacuoles Microvilli Animal cell structure
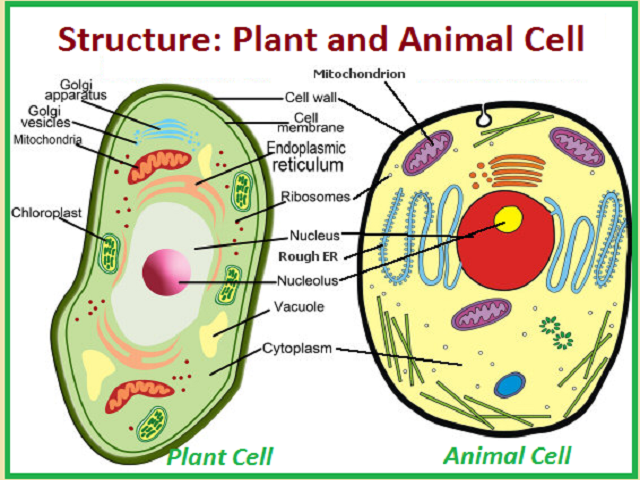
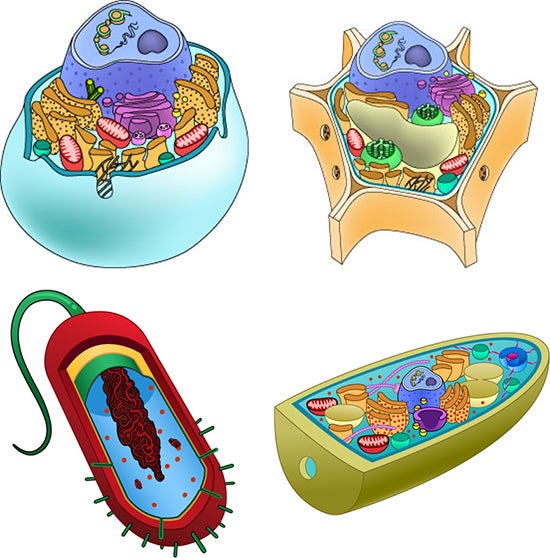
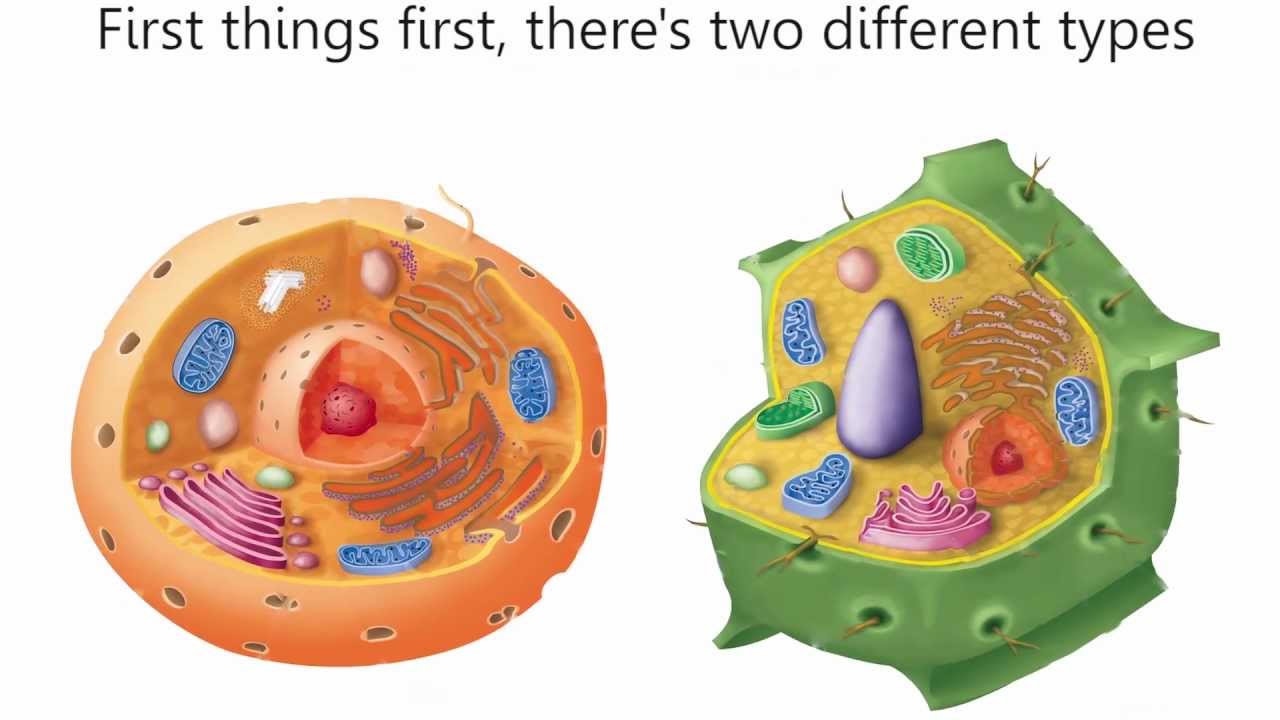
Parts of the animal cells. Animal Cell: Types, Diagrams and Functions - Embibe The eukaryotic cells have cell organelles lacking in prokaryotic cells except for the ribosomes. The animal cells consist of the centriole, which carries out cell division. The animal cells have an organized nucleus with a nuclear envelope. Along with that, it possesses locomotory structures. Cell Parts 101: Plant And Animal Cell Helpful Study Guides An animal cell will typically range between 10 and 30 micrometers in length, while a plant cell can reach 100 micrometers in length. Plant cells are larger because they contain vacuoles that store water. Animal cells also have vacuoles, but these organelles aren't used to store water. The cell wall is another important difference. What are cells? Animal and plant cells - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize They have the same cell components as animal cells: a nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm and mitochondria. They also have these extra three as well: Cell wall: a tough outer layer of the... What are the 13 parts of an animal cell? - BYJUS The thirteen parts of an animal cell are vacuoles, cytoplasm, vesicles, centrioles, ribosomes, nuclear membrane, cell membrane, cytoskeleton, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, Golgi apparatus and nucleus. You can read about the Plant Tissues - Classification, Definition, Types in the given link. Further readings:
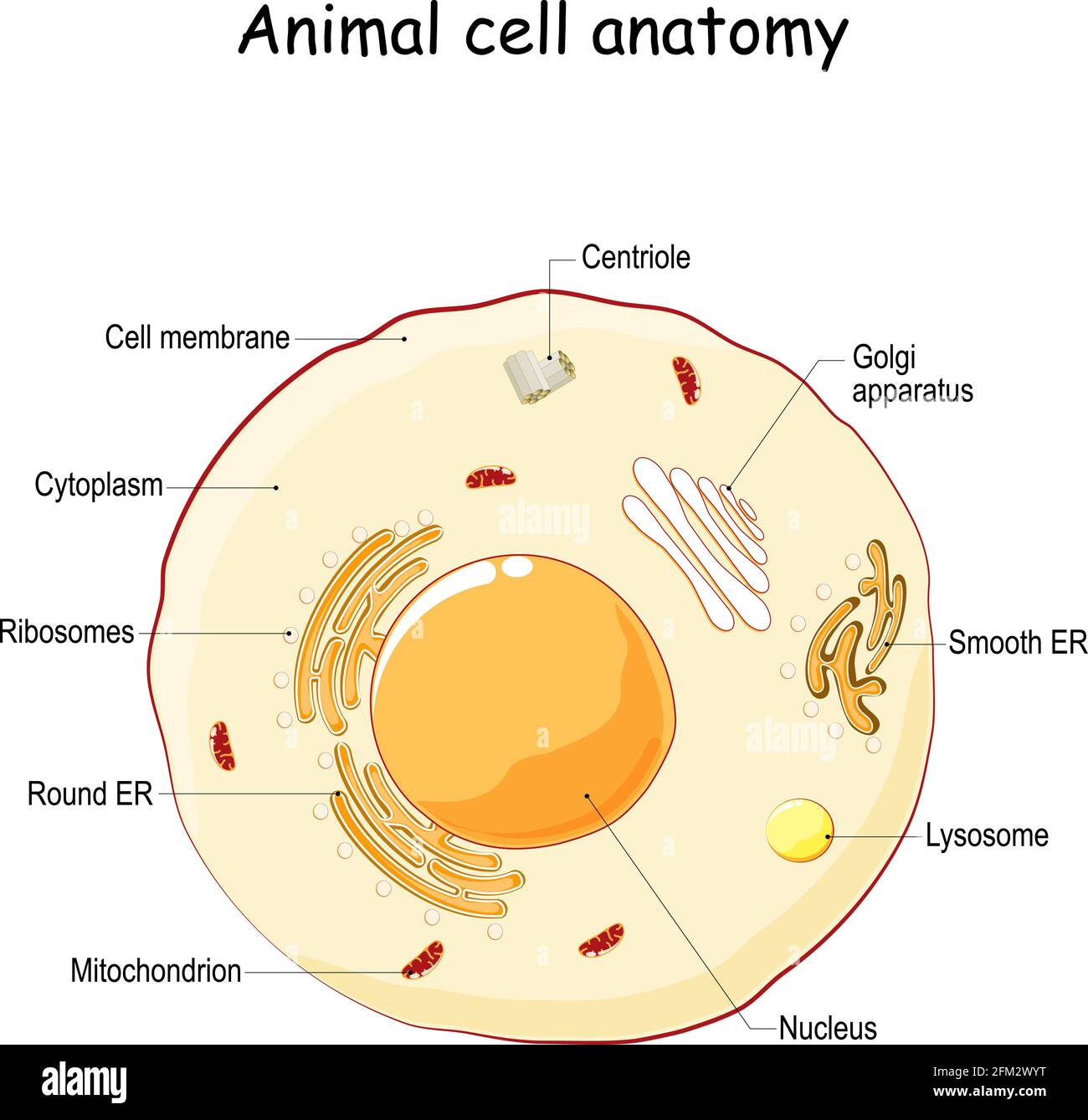
Animal Cell Parts - Biology Wise What Are the Various Parts of an Animal Cell? Cell Membrane: The cell membrane is the outermost part of the cell, which encloses all the other cell organelles. This organ controls the influx of nutrients and minerals in and out of the cell. Cell Cytoplasm: Cytoplasm is supposed to be the matrix or gel-like substance/fluid present inside the cell. Animal Cell - Structure, Function, Diagram and Types - BYJUS There are numerous types of animal cells, each designed to serve specific functions. The most common types of animal cells are: Skin Cells Melanocytes, keratinocytes, Merkel cells and Langerhans cells Muscle Cells Myocyte, Myosatellite cells, Tendon cells, Cardiac muscle cells Blood Cells Leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelet Nerve Cells Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are all made up of at least one eukaryotic cell. In contrast, bacteria and archaea are made up of a single prokaryotic cell. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane (also called a plasma membrane). The cell membrane is the boundary that separates the inside of the cell from the outside of the cell. Animal cell parts and their function - WhatMaster The animal cell is fundamentally composed of a plasma membrane, a nucleus, and a cytoplasm. Next, we will explain each one in detail. Plasma membrane The plasma membrane is the outer covering of the cell, through which contact is made with the external environment. It consists of two sheets of lipids, lipid bilayer, and membrane proteins.
Complete Guide! Animal Cell Diagram, Parts of an Animal, Plant Cell Vs ... The organelles found in most animal cells include the nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes, lysosomes, vacuoles, centrosome, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus. Let's discuss these organelles in detail: Cell Membrane This is the outer barrier of the animal cell. It controls what goes in and out of a cell. Animal Cells | Basic Biology There are heaps of different types of animal cells and these are just a few from common tissues like skin, muscle, and blood. Skin cells The skin cells of animals mostly consist of keratinocytes and melanocytes - 'cyte' meaning cell. Keratinocytes make up around 90% of all skin cells and produce a protein called 'keratin'. Animal Cells for Kids (Explained!) - Education site Animal cell parts and their jobs. Animal cells contain a lot of parts or "organelles", and each one has a specific job to accomplish to make sure the cell is healthy and plays a role in keeping the body functioning. Here is a list of organelles in alphabetic order. As you read through each of the organelles, you will begin to understand how ... Plant and Animal Cell: Definition, Structure, Differences - Embibe Exams Both plant and animal cells have similar types of architecture. They are made up of cell boundaries, cytoplasm, nucleus and several cellular organelles. Different Plant and Animal Cell Parts Fig: Chloroplast Practice Exam Questions Fig: Mitochondria Fig: Nucleus Fig: Plasma membrane Fig: Centriole Differences Between Plant and Animal Cell
Parts of an Animal Cell : 8 Steps (with Pictures) - Instructables Step 4: Create the Cross Section of the Cell. Once you have centered the smaller sphere inside of the larger sphere, draw a box around the spheres and lock them. To create the cross-section, drag and drop a box onto the grid. Change the height to 4", the width to 11", and the length to 6". Then change the box to a "hole box by selecting ...
What Is An Animal Cell? Discover the Parts of a Eukaryotic Cell & the ... Major Parts of an Animal Cell Cell membrane - controls what goes in and out of a cell Nucleus - controls the cell's activities Cytoplasm - contains enzymes Mitochondria - produce energy Ribosomes - produce protein Let's look at each of these in more detail. Cell membrane All animal cells have a plasma membrane.
Animal cells - Cell structure - AQA - BBC Bitesize Animal cells. Almost all animals and plants are made up of cells. Animal cells have a basic structure. Below the basic structure is shown in the same animal cell, on the left viewed with the light ...
Animal Cells: Lesson for Kids - Video & Lesson Transcript - Study.com Parts of an Animal Cell When you picture a cell, you probably think of a circle shape. Actually, animal cells come in all different shapes like the long, thin muscle cell, and the spiky nerve cell.
Parts of an animal cell ️ Postposmo | Postposm 2 parts of an animal cell 2.1 Plasma membrane 2.2 Core 2.3 Cytoplasm 2.4 Mitochondria 2.5 Lysosome 2.6 Golgi apparatus 2.7 Endoplasmic reticulum 2.8 Centriole 2.9 chromatin 2.10 How is an animal cell different from a plant cell? What is an animal cell?
Parts of an Animal Cell and Their Functions - noteshippo.com These are the most common kinds of cells seen in animals: Skin Cells: "Skin cells" can refer to any of the four main types of cells that make up the epidermis. The Langerhans cells, Merkel cells, keratinocytes, and melanocytes make up this group. The way each type of skin cell works affects how the skin is put together and how it works as a whole.
Learn the Parts of the Animal Cell (Coloring) - Biology LibreTexts Color according to the directions below; the numbers correspond to the numbers on the cell diagram. The cell membrane surrounds the cell and acts as a barrier. It controls what comes in and out of the cell. Color the membrane light brown. The membrane can have structures on its surface that help the cell move, or move particles within the body.
Parts of the animal cell | AgroCorrn List of the parts of the animal cell In order to know the main characteristics of the animal cell, it is convenient to begin by learning what its parts and functions are. In summary, this is the list of the parts of the animal cell : Core Plasma membrane Cytoplasm Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Centrosome Cilia and flagella Mitochondria
Animal Cell Definition, Components And Structure | Biology Topics Animal Cell Definition: Animal cells, which are the fundamental units of life in the Animal Kingdom, are eukaryotic cells. This means that they contain a true (membrane-bound nucleus) along with other membrane-bound organelles. All these work together to perform specific functions that are needed for the proper functioning of the cell. Although plant cells are ...
What are the Parts of an Animal Cell? - YouTube Learn about all of the parts that make up an animal cell, and their function. We hope you are enjoying this video! For more in-depth learning, check out Miacademy.co (...
Animal Cell - Functions and Structure of Animal Cells - VEDANTU In biological terms, an animal cell is a typical eukaryotic cell with a membrane-bound nucleus with DNA present inside the nucleus. It comprises other cellular structures and organelles which helps in carrying out some specific functions required for the proper functioning of the cell.
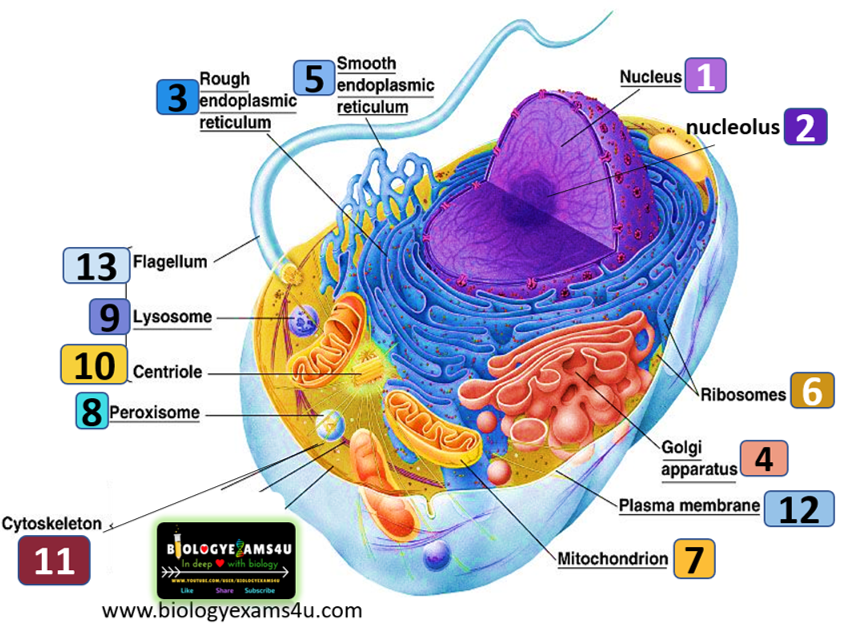
Cell City Analogy. Learn the Cell Parts - biologyexams4u.com 2) Mitochondrion: In a city, it is the "Power plant" where energy or electric current is supplied to different parts of the city for day-to-day activities. It is the powerhouse of the cell producing energy by cellular respiration thus providing energy for all cellular activities. 3) Cytoplasm: In a city, it can be compared to the "premise ...
Animal Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram List of Animal cell organelles Plasma membrane (Cell membrane) Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Golgi apparatus (Golgi bodies/Golgi complex) Lysosomes Cytoskeleton Microtubules Centrioles Peroxisomes Cilia and Flagella Endosome Vacuoles Microvilli Animal cell structure
15 parts of the animal cell Flashcards | Quizlet Cytoplasm This is the area that contains the important structures of the cell Ribosomes These are the 'factories' where proteins are put together, these are also inside the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Vacuole The 'warehouse' of the cell where materials are stored Mitochondria These are the 'power plants' of the cell where energy is made Chromatin
A Quick Guide to the Structure and Functions of the Animal Cell An animal cell is the smallest unit that makes up the varied tissues of animal species. There are hundreds of cell types in a developed organism, which are specific to their location and function. The red blood cells make up the blood, while the nerve cells make up the nervous system tissues. Likewise, there are more than 200 types of cells in ...





















Post a Comment for "44 parts of the animal cells"